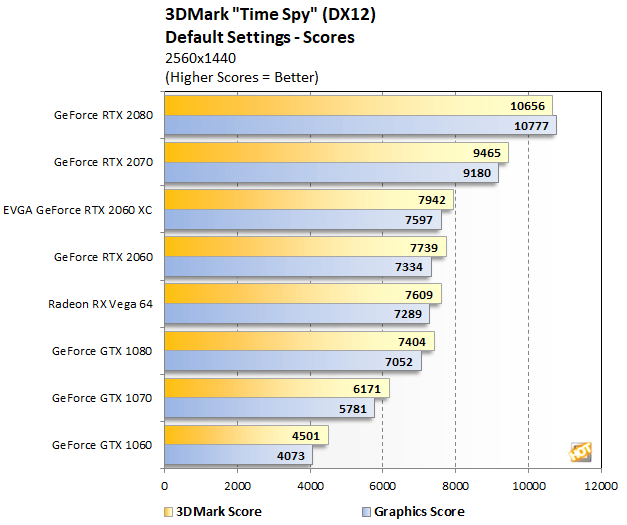3DMark Time Spy is a synthetic DirectX benchmark test from Futuremark. It features a DirectX 12 engine built from the ground up to support bleeding-edge features like asynchronous compute, explicit multi-adapter, and multithreading. Time Spy is designed to test the DirectX 12 performance of the latest graphics cards using a variety of techniques and varied visual sequences. This benchmark was developed with input from AMD, Intel, Microsoft, NVIDIA, and the other members of the Futuremark Benchmark Development Program, to showcase the performance and visual potential of graphics cards and other system resources driven by close-to-the-metal, low-overhead APIs.
 |
| 3DMark Time Spy |
|
Direct X 12 Performance |
|
We saw more of the same in 3DMark Time Spy. In this DX12-benchmark, the EVGA GeForce RTX 2060 XC continues to finish ahead of NVIDIA’s RTX 2060 and the GeForce GTX 1080, and hangs with AMD's Radeon
Vega 64 as well.
|

|
| Futuremark 3DMark Fire Strike |
| Synthetic DirectX Gaming |
|
3DMark Fire Strike has multiple benchmark modes: Normal mode runs at 1920x1080, Extreme mode targets 2560x1440, and Ultra mode runs at a 4K resolution. GPU target frame buffer utilization for normal mode is 1GB and the benchmark uses tessellation, ambient occlusion, volume illumination, and a medium-quality depth of field filter. The more taxing Extreme mode targets 1.5GB of frame buffer memory and increases detail levels across the board. Ultra mode is explicitly designed for high-end and CrossFire / SLI systems and cranks up the quality even further. GT 1 focuses on geometry and illumination, with over 100 shadow casting spot lights, 140 non-shadow casting point lights, and 3.9 million vertices calculated for tessellation per frame. GT2 emphasizes particles and
GPU simulations.

3DMark Fire Strike


In the DX11-based Fire Strike benchmark, the EVGA GeForce RTX 2060 XC continues to outrun the “stock” NVIDIA card, but the 1080 and Vega 64 pull out in front.
 |
|
3DMark Port Royal |
|
DXR Ray Tracing |
|
According to UL, the recently-released 3DMark Port Royal test is a “realistic and practical example of what to expect from
ray tracing in upcoming games”. The test incorporated ray tracing effects, running in real-time, at a resolution of 2560 × 1440. 3DMark Port Royal was developed with input from AMD, Intel, NVIDIA, and other leading technology companies, and while it can technically run on any DX12-class GPU with
DXR support, it is only NVIDIA’s Turing-based GeForce RTX cards that have ray tracing-enabled drivers at the moment.
In the new 3DMark Port Royal Ray Tracing benchmark, the EVGA GeForce RTX 2060 XC beats NVIDIA’s design – as you would expect – and lands similarly, with respect to all of the other ray tracing-enabled cards in this test.