NVIDIA nForce 780a SLI Motherboard Round-Up
How We Configured Our Test Systems: When configuring our test systems for this article, we first entered their respective system BIOSes and set each board to its "Optimized" or "High performance Defaults". We then saved the settings, re-entered the BIOS and set memory timings for either DDR2-1066 (AMD) with 5,5,5,15 timings or DDR3-1333 with 7,7,7,20 timings (Intel). The hard drives were then formatted, and Windows Vista Ultimate was installed. When the Windows installation was complete, we updated the OS, and installed the drivers necessary for our components. Auto-Updating and Windows Defender were then disabled and we installed all of our benchmarking software, defragged the hard drives, and ran all of the tests.
|
|
System 1: Asus P5E3 Premium 2x1GB Corsair DDR3-1800 GeForce 8800 GTX WD740 "Raptor" HD Windows Vista Ultimate |
System 2: Asus M3N-HT Deluxe Asus CrossHair II Formula GeForce 8800 GTX WD740 "Raptor" HD Windows Vista Ultimate |
|
|
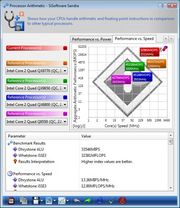
We began our testing with SiSoftware's SANDRA XII, the System ANalyzer, Diagnostic and Reporting Assistant. We ran three of the built-in subsystem tests that partially comprise the SANDRA XII suite with an AMD Phenom X4 9850 processor installed in the Asus M3N-HT Deluxe motherboard (CPU Arithmetic, Memory Bandwidth, and Memory Latency). All of the scores reported below were taken with the processors running a clock speed of 2.5GHz, with 2GB of DDR2-1066 RAM installed. Please note however, that when the nForce 780a SLI IGP is used, 256MB of system memory is reserved for the IGP, which brings down the total amount of availabl memory and bandwidth.
The SiSoft SANDRA results above show how utilizing the nForce 780a SLI IGP affects CPU and memory performance. If you flip through the various results above, you'll see that the CPU Arithmetic and Multimedia benchmarks show very little variation in the two different configurations. The Memory Bandwidth test, however, shows the system with discreet graphics having a 700MB/s advantage in terms of peak bandwidth. This is direct result of the IGP sharing memory with the system. We'll show how this affects overall system performance as well on the pages ahead.