AMD Barcelona Architecture Launch: Native Quad-Core
 It has been quite a while since AMD launched a truly new CPU core architecture. It was way back in September of 2003 that the first "K8" based desktop processors arrived in the form of the single-core Athlon 64 and Athlon 64-FX. And while the company has launched a slew of new desktop, server, and mobile processors since then, there haven’t been any major changes made to the base CPU architecture. AMD did make some modifications to the execution core as they introduced processors for different sockets or with different L2 cache sizes, but overall the architecture remained largely unchanged.
It has been quite a while since AMD launched a truly new CPU core architecture. It was way back in September of 2003 that the first "K8" based desktop processors arrived in the form of the single-core Athlon 64 and Athlon 64-FX. And while the company has launched a slew of new desktop, server, and mobile processors since then, there haven’t been any major changes made to the base CPU architecture. AMD did make some modifications to the execution core as they introduced processors for different sockets or with different L2 cache sizes, but overall the architecture remained largely unchanged.
Today’s Athlon 64 X2 processors have quite a lot in common with those initial Athlon 64s. The first major change came when AMD built the first native dual-core X2, which was essentially a pair of Athlon 64 execution cores and a single memory controller on a single die. Then AMD surgically removed the original DDR memory controller and replaced it with a DDR2 controller with the transition to socket AM2 in May of last year. But in the almost four year span since the launch of the initial Athlon 64 processors up until today, the technology employed in the processors was essentially the same.
September 10, 2007 is a big day for AMD, however. Today is the day AMD is officially taking the wraps of their native quad-core Barcelona-based Opteron processors. While the Barcelona core does still borrow heavily from their last-gen processors, it incorporates a number of enhancements for increased performance and power efficiency.
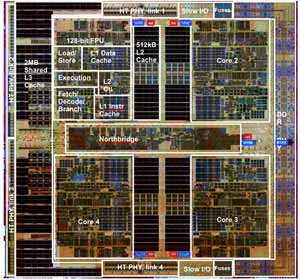
The new processors being launched today are the Quad-Core AMD Opteron Processor model numbers 8350, 8347, 8347 HE, 8346 HE, 2350, 2347, 2347 HE, 2346 HE, and 2344 HE. The image above illustrates the layout of the actual Barcelona die and highlights the functional blocks within the CPU. Although the processors being launched today have some different capabilities, namely their ability to be used in different multiprocessors configurations, they only differ in their compliment of active HyperTransport links (visible around the edge of the die shot).
| AMD OPTERON PROCESSOR TECH SPECS COMMON TO THIRD GENERATION CPUs (X3XX SERIES): | |
| L1 Cache Sizes: | 64K of L1 instruction and 64K of L1 data cache per core (512KB total L1 per processor) |
| L2 Cache Sizes: | 512KB of L2 data cache per core (2MB total L2 per processor) |
| L3 Cache Size: | 2MB dynamically shared |
| MC Type: | NEW Integrated 128-bit wide memory controller, capable of being configured for dual 64-bit channels for simultaneous read/writes |
| MC Speed: | Up to 1.8GHz with Dual Dynamic Power Management (1.6GHz on legacy Socket F (1207) motherboards) |
| Types of Memory: | Registered DDR2 up to PC2 5300 (667MHz) |
| HyperTransport 1.0 Links (8000s): | 3 total, 3 coherent (8-way capable) |
| HyperTransport 1.0 Links (2000s): | 3 total, 1 coherent (2-way capable) |
| HyperTransport 1.0 Spec: | 1GHz full duplex (2000MT/s) |
| Packaging: | Socket F (1207) OLGA (1207-pin organic land grid array) |
| Fab location: | AMD's Fab 36 wafer fabrication facilities in Dresden, Germany |
| Process Technology: | 65nm Silicon on Insulator (SOI) |
| Approximate Transistor count: | approx. 463 million |
| Approximate Die Size: | 285 mm2 |
| Max Ambient Case Temp: | 70 degrees Celsius |
The chart above is a breakdown of the technical specifications common to all Barcelona-based Opteron processors. Each of the four cores is outfitted with 64K of L1 instruction and 64K of L1 data cache, for a total of 512K of L1 cache per CPU. The L2 cache compliment of each core is 512K, for a total of 2MB. New to the Barcelona core is 2MB of dynamically shared L3 cache. Unlike L1 and L2 caches, which are exclusive to each execution core (data in Core 1’s L2 cache cannot be accessed by Core 3, for example), the L3 cache is shared among all the cores. Also new to Barcelona-based Opterons is a 128-bit wide memory controller that can be configured as dual independent 64-bit channels to allow for simultaneous read and write memory operations.
At present, the new AMD Opterons will be built in AMD’s Dresden, Germany facility using the company’s 65nm SOI (silicon on insulator) manufacturing process. Each Barcelona die is comprised of approximately 463M transistors (about 119M less than Intel’s quad-core Kentsfield) and is about 285mm2 in size.
| AMD OPTERON PROCESSOR TECH SPECS BY MODEL NUMBER: | |||||
|
Processor
|
OPN
|
CPU Freq. / NB Freq.
|
*ACP*
|
TDP
|
Voltage
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 8350
|
OS8350WAL4BGE
|
2.0 GHz / 1.8 GHz
|
75w
|
95w
|
1.2v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 8347
|
OS8347WAL4BGE
|
1.9 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
75w
|
95w
|
1.2v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 8347 HE
|
OS8347PAL4BGE
|
1.9 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
55w
|
68w
|
1.15v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 8346 HE
|
OS8346PAL4BGE
|
1.8 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
55w
|
68w
|
1.15v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 2350
|
OS2350WAL4BGE
|
2.0 GHz / 1.8 GHz
|
75w
|
95w
|
1.2v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 2347
|
OS2347WAL4BGE
|
1.9 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
75w
|
84w
|
1.2v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 2347 HE
|
OS2347PAL4BGE
|
1.9 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
55w
|
68w
|
1.15v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 2346 HE
|
OS2346PAL4BGE
|
1.8 GHz / 1.6 GHz
|
55w
|
68w
|
1.15v
|
|
AMD Opteron Processor Model 2344 HE
|
OS2344PAL4BGE
|
1.7 GHz / 1.4 GHz
|
55w
|
68w
|
1.15v
|
Above is a list of the nine different quad-core Opterons being launched today along with their respective core and Northbridge frequencies, power consumption characteristics, and default voltages. As you can see, the highest clocked model will arrive at 2.0GHz, but with a TDP of only 95w.