AMD Ryzen 9 3950X Review: A 16-Core Zen 2 Powerhouse
AMD didn’t hit the initial September release target Dr. Su had originally mentioned for the Ryzen 9 3950X, citing stronger than anticipated demand for currently shipping products. The Ryzen 9 3950X is due to ship in a coupe of weeks though, alongside those beastly new Threadrippers, and we were lucky enough to take one for a spin. We don’t want to spoil the rest of the review for you right out of the gate, but as you’ll see, the new AMD Ryzen 9 3950X is absolutely worth the wait...
|
| # of CPU Cores | 16 |
| # of Threads | 32 |
| Base Clock | 3.5GHz |
| Max Boost Clock | Up to 4.7GHz |
| Total L1 Cache | 1MB |
| Total L2 Cache | 8MB |
| Total L3 Cache | 64MB |
| Unlocked | Yes |
| CMOS | TSMC 7nm FinFET |
| Package | AM4 |
| PCI Express Version | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| Thermal Solution (PIB) | Cooler Not Included, Liquid Cooling Recommended |
| Default TDP / TDP | 105W (65W Optional via Ryzen Master) |
| System Memory Specification | 3200MHz |
| System Memory Type | DDR4 |
| Memory Channels | 2 |
The AMD Ryzen 9 3950X’s main features and specifications are listed above. From a design standpoint, there’s nothing to really differentiate the Ryzen 9 3950X from the Ryzen 9 3900X that launched a few months back. Both processors feature a pair of CPU chiplets, linked to an IO die on a single package. They're both destined for AMD’s socket AM4 and both feature a 105W TDP, though that's configurable now thanks to a new, more power-friendly ECO mode that brings the TDP down to 65W. Unlike the Ryzen 9 3900X, however, the Ryzen 9 3950X has all 8-cores enabled in each of its CPU chiplets and its frequencies are different too. The Ryzen 9 3950X has base and boost clocks of 3.5GHz and 4.7GHz, respectively, while the 3900X has a higher 3.8GHz base clocks, but lower 4.6GHz boost clock.
Save for its specific markings, the Ryzen 9 3950X looks just like any other 3rd Generation Ryzen 3000 series desktop processor. They use the same AM4 socket and are compatible with the same motherboards, memory, coolers, etc. From the top and bottom, there’s not much to see that’ll appear any different than any of AMD’s mainstream desktop processors of the last few generations.
As mentioned, the CPU cores at the heart of the Ryzen 9 39050X are grouped into two, 7nm 8-core chiplets, each with dual, four-core compute complexes (CCX). Those chiplets link to an IO die (manufactured at 12nm) that houses the memory controller, PCI Express lanes, and other off-chip IO. Instead of having one large die like most previous-gen processors, the Ryzen 3000 series is comprised of multiple chiplets, that are linked together via AMD’s Infinity Fabric.
If you check out the CPU-Z details for the new Ryzen 9 3950X, you’ll see that the chip is code named “Matisse” and just like the previously-launched Ryzen 3000 series processors, it is based on stepping 0 of revision MTS-B0. The processor has 32K of L1 data cache per core, and 32K of L1 instruction cache per core, which is actually half that of second-gen Ryzen. The re-configured L1 cache, however, has 8-way associativity. The 512K of L2 cache per core is also 8-way associative, and there is 16MB of shared L3 cache per CCX, which is 16-way associative. On the 16-core (32-thread) Ryzen 9 3950X, that brings total cache up to a whopping 73MB, while the 12-core 3900X tops out at 70MB and 8-core processors max out at 36MB.
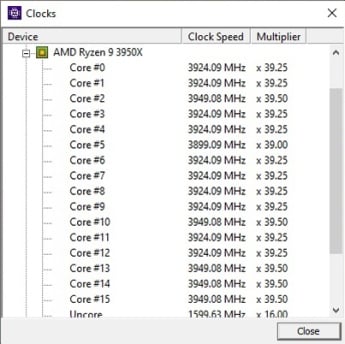
Like all other modern processors, frequencies and voltages scale up and down dynamically on the Ryzen 9 3950X based on the given workload, hence the funky clocks and voltages in the above screenshots. We should note that Ryzen 3000 series processors can ramp clocks faster than previous-gen parts with the proper OS and driver support now, which in turn can further enhance performance. The upcoming November Windows Update will also incorporate changes to better schedule threads on many-core processors like the Ryzen 3000 series and it'll favor the fastest cores as well.
During testing, we rarely saw the Ryzen 9 3950X hit its maximum 4.7GHz boost clock, but it often exceeded 4.62GHz - 4.65GHz. And the processor was almost always operating well north of its base clock. Even after extended periods running full-bore with multi-threaded workloads, the 3950X typically saw all cores tickling the 4GHz mark.
With that foundation laid, let's get into some benchmarks shall we?