AMD Ryzen 7 2700 And Ryzen 5 2600 Review: Great Value, Solid Performance
We’ve got the main features and specifications for the first wave of 2nd Generation Ryzen processors outlined in the tabled below. Take a look at what we’re dealing with here, then we’ll dive in a little deeper and see where the parts fit in the current desktop processor landscape...
|
There's not much to see externally to differentiate the Ryzen 7 2700 And Ryzen 5 2600 from their higher-end counterparts. All of the processors in the 2nd Gen Ryzen line-up use the same die, packaging, heat-spreader, and pin-out, and only differ in the actual branding that's laser-etched on top. The packaging is identical, though if you’ve got some time on your hands and are feeling a little frisky, you can verify and count the 1,331 pins on their undersides.
These "non-X" variants of AMD's 2nd Gen Ryzen processors only differ in their default target frequencies and TDP. Whereas the 8-core Ryzen 7 2700X has base and boost clocks of 3.7GHz and 4.3GHz, respectively, with a 105W TDP, the Ryzen 7 2700 comes in at 3.2GHz / 4.1GHz with only a 65W TDP. The 6-core Ryzen 5 2600 also has lower clocks and a lower TDP than the 2600X, but its worth noting that its base clock is actually 200MHz higher than the 2700. This frequency differential will result in higher performance with lightly-threaded workloads and is something to keep in mind if your use case doesn't require the additional cores afforded by a Ryzen 7 2700.


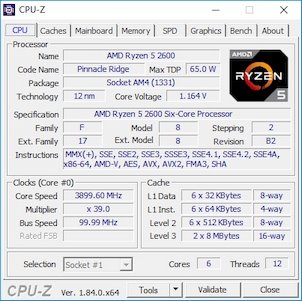

CPU-Z Details - Ryzen 7 2700 (Top), Ryzen 5 2600 (Bottom)
If you check out the CPU-Z details for the Ryzen 7 2700 and Ryzen 7 2600, you’ll see that the chips are code named “Pinnacle Ridge” and they’re based on stepping 2, revision B2 of AMD's Zen+ design. In terms of their configurations (disregarding frequencies) not much changes. The processors have up to 256K of L1 data cache (32K per core), up to 512K of L1 instruction cache (64K per core), up to 4MB of L2 cache (512K per core), and up to 16MB of shared L3 cache. The die size of the processor is roughly 213mm2 and it is comprised of approximately ~4.8 billion transistors. Like all other modern processors, frequencies and voltages scale up and down dynamically based on the given workload, hence the funky clocks and voltages in the above screenshots.
In terms of their architecture and feature set, AMD’s 2nd Generation Ryzen processors don’t stray too far from the originals. SenseMI, Pure Power, and XFR are all here, interconnected by AMD Inifinity Fabric. We won’t cover all of those technologies again though, since we've already done so in the past. Check out our original coverage for those details. And, of course, check out our 2nd Gen Ryzen launch article for the full scoop on the Ryzen 7 2700X And Ryzen 5 2600X and all of the enhancements that came with Zen+, which were covered in the piece.
For now, let's see how these puppies perform...








