Intel Core 2 Extreme QX6800
Introduction and Related Information

 Hot on the heals of the holiday weekend, Intel is launching a new flagship quad-core processor targeted at hardcore power users and PC enthusiasts. As its name implies, the new Core 2 Extreme QX6800 has frequency parity with its dual-core counterpart, the Core 2 Extreme X6800 - sans the "Q". At 2.93GHz this makes the Core 2 Extreme QX6800 Intel's highest clocked quad-core desktop processor to date.
Hot on the heals of the holiday weekend, Intel is launching a new flagship quad-core processor targeted at hardcore power users and PC enthusiasts. As its name implies, the new Core 2 Extreme QX6800 has frequency parity with its dual-core counterpart, the Core 2 Extreme X6800 - sans the "Q". At 2.93GHz this makes the Core 2 Extreme QX6800 Intel's highest clocked quad-core desktop processor to date.
Other than its higher frequency though, the Core 2 Extreme QX6800 doesn't differ from Intel's previous high-end quad-core processor, the 2.66GHz Core 2 Extreme QX6700, in any way. But what the QX6800's higher core frequency offers is an answer to any performance advantage the higher clocked X6800 had when running single-threaded applications.
To see just how much power the new Core 2 Extreme QX6800 had lurking under its unassuming heat spreader, we installed one into a 975X-based test bed an took it for a spin. Read on to see how it did. Just hide your tax return or your going to want to give Big Blue a big chunk of what Uncle Sam just gave back.
|
|
|
Over the course of the past year or so, we have posted a wealth of information related to Intel's Core microarchitecture and Core 2 Duo and Extreme processors here at HotHardware.com. For more background on the technologies employed by the Core microarchitecture and Intel's platform as a whole, we suggest taking a look at few of these related articles. They contain detailed explanations of some of the features common to Intel's legacy products, compatible chipsets, and the new Core 2 Duo and Core 2 Extreme processors:
- Core 2 Extreme QX6700 Review
- Core 2 Extreme QX6700 IDF Preview
- Core 2 Duo E6700 & Extreme X6800 Evaluation
- AMD Athlon 64 X2 6000+ (AMD's most recent competitive launch)
- Pentium Extreme Edition 965 Evaluation
- Pentium Extreme Edition 955 & i975X Express Chipset Evaluation
- Pentium Extreme Edition 840 Preview
- Pentium D 820 & i945G/P Evaluation
We cover some specifics regarding Intel's 65nm manufacturing process in our 955XE / i975X evaluation and outline Intel's AMT (Active Management Technology) and IVT (Intel Virtualization Technology), among other things inherent to the Core microarchitecture, in our Core 2 Duo E6700 & Extreme X6800 Evaluation . The other articles listed above will also give you some background as to how the Core 2 has matured these last few months, leading up to today's official launch of the new quad-core Core 2 Extreme QX6800 processor.
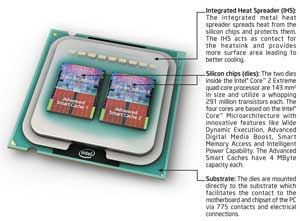
Beyond the clock speed bump, there really isn't too much more to know about the QX6700 versus the QX6700 or X6800, other than the fact that the chip is simply a pair of dual-core, Core 2 Extreme X6800 processor cores clocked at 2.93GHz, on a single package substrate, sharing a single 1066MHz QDR (Quad Data Rate) System Bus. That's four cores and 8MB of on-die cache all in a single LGA775 socket. In other words, double the cores, and double the cache of Intel's high-end Core 2 Duo dual-core processors. Of course that also takes the QX6800's TDP (Thermal Design Power) up a notch from the Core 2 Duo's 65-75 Watt range to roughly double that at 130 Watts. This puts this new Intel quad-core CPU within range of Intel's legacy Pentium Extreme Edition 965 dual-core chip from a power and heat dissipation perspective. That's not too bad when you consider how much faster the architecture has proven itself to be and the fact that we're talking four cores in total here, versus only two in the Pentium EE 965.